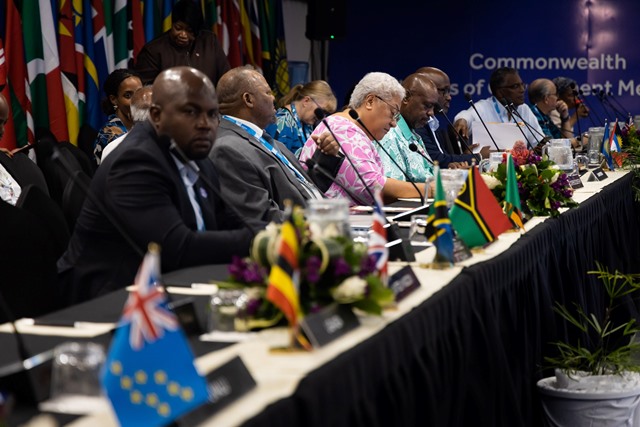
The Small States session held at the 2024 CHOGM. [photo: Samoan Government CHOGM]
The Small States session held at the 2024 CHOGM. [photo: Samoan Government CHOGM]
[Derek McDougall is a member of the Round Table’s International Advisory Board and brings to an end his Samoa Diary series from the Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting in Samoa.]
There is a disjunction between the Samoa CHOGM (Commonwealth Heads of Government Meeting) as reported in the media in Australia and the United Kingdom (UK) and CHOGM as actually experienced.
In the Australian media the focus was on CHOGM as an arena for tensions between Australia and the Pacific island countries (PICs) over climate action, also raising the spectre of increasing Chinese engagement with these countries. In the British media the emphasis was on the demand coming from the Caribbean for the UK to undertake reparations for the historical injustice of slavery.
There is an important civil society dimension to the Commonwealth. It is not just about governments. The first part of CHOGM was about Commonwealth civil society, pre-eminently in the People’s Forum over two days. There were also forums for women, youth and business, and numerous side events, often dealing with issues relating to themes being advanced in the forums. In the People’s Forum the focus was on climate justice, health justice and freedom of expression. On the final day of CHOGM the civil society representatives were able to take up these issues in a forum with ministers organised by the Commonwealth Foundation, the umbrella for Commonwealth civil society and the link to the Commonwealth Secretariat.
For the intergovernmental Commonwealth the focus initially was on meetings of foreign ministers leading up to the opening with King Charles on Friday and then the actual leaders’ meeting on Saturday, the final day of CHOGM. Politically the emphasis was on small states, especially the small island developing states (SIDS). At one level the Samoa CHOGM was an attempt to advance the Antigua and Barbuda Agenda for SIDS (ABAS), agreed to at the decennial meeting of SIDS held in May.
The broad goal of ABAS is sustainable development, giving particular attention to climate change, economic vulnerabilities, and the impact of exogenous shocks. Among the recommended actions are improved terms for development finance, stronger climate action (including better climate finance), greater attention to conservation and sustainable use of the oceans, measures for disaster risk reduction, and improved health systems.
In the Samoa CHOGM Communiqué there is specific support for ABAS (para. 3). The various sections covering resilience in relation to societies and peoples, democratic institutions, the environment and economies are broadly in line with ABAS, while not being only SIDS issues. Commonwealth civil society would welcome the statement. On climate justice, the communiqué noted the importance of this concept ‘for some’ (para. 31).
Read the Samoa Diary series from Derek McDougall
As reflected in the Communiqué, there is an avoidance of geopolitical issues unless there is strong support for a Commonwealth country in relation to a neighbour: Guyana against Venezuela, Belize against Guatemala (territorial disputes); Cyprus against North Cyprus (dispute over governance); Bangladesh against Myanmar (the Rohingya refugees). Haiti gets a mention in the Leaders’ Statement because of some Commonwealth members contributing to peacekeeping there. There is no reference to issues concerning China, Russia-Ukraine or the Middle East, or AUKUS for that matter. Among Commonwealth countries the tensions between India and Canada are not mentioned, with both countries having relatively low-level representation at CHOGM. Nor is there any point about the UK-Mauritius agreement over Chagos. Zimbabwe did not feature either.
Overall, the SIDS should be well satisfied with the outcome of CHOGM. With 33 small states out of 56 Commonwealth members, including 24 SIDS, they were well placed to influence the outcome. The Apia Commonwealth Ocean Declaration was also a success for the SIDS. Samoa was the first SIDS CHOGM, as well as the first PIC CHOGM. The CHOGM in 2026 will also be in a SIDS: Antigua and Barbuda.
The future of the Commonwealth might be as a SIDS plus organisation. There is a strong synergy between the PIC and Caribbean members, with the Indian Ocean members and Malta also important in this respect. The ‘plus’ includes Africa, with the strong Commonwealth focus in that region attracting new African members in recent times (Mozambique, Rwanda, Cameroon, Togo, Gabon). It is also Africa’s turn to have one of its own as Secretary-General, with Shirley Botchwey (foreign minister of Ghana) being the successful candidate.
The SIDS have regional organizations such as the Pacific Islands Forum (also with Australia and New Zealand), CARICOM and the Indian Ocean Commission (also with France through Réunion). There is also the SIDS only global organization, the Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS). The Commonwealth is unique in that it enables the SIDS to work cross-regionally but also with other small states and the Global South members generally, as well as with the Global North members (some of which are in the southern hemisphere). It is a context where the SIDS/small states and the Global South can try to influence some significant countries in the Global North, although not the major world powers. In turn the Global North members can try to win support on various issues themselves, particularly in UN contexts where numbers matter. We should see the impact of this interaction in the first instance with the Azerbaijan COP in November.
A taster of articles by Derek McDougall for the Round Table
While Canada and India were underrepresented at CHOGM, the leaders of Nigeria and South Africa were also absent. Prime Minister Narendra Modi and President Cyril Ramaphosa were at the BRICS meeting in Moscow. Only about 20 government heads attended CHOGM.
Some of the African countries make it difficult to implement the principles of the Commonwealth Charter concerning democracy and human rights. Commonwealth civil society strongly supports the Charter. Justice Michael Kirby of Australia said at the People’s Forum that the Commonwealth is a values-based organisation, or it is nothing. He advocates having a Commonwealth human rights commissioner. The Commonwealth Ministerial Action Group might become more active on these issues. To date the Commonwealth has been very circumspect in dealing with the poor record of some of its members. While there is an argument for ‘engagement’ with such members, the modalities for engagement might be worked out better.
In terms of advancing the civil society agenda, the adoption of the Commonwealth Principles on Freedom of Expression and the Role of the Media was a success. But there is still a long way to go.
Despite the tensions over climate action Australia had a successful CHOGM, with both Prime Minister Anthony Albanese and Foreign Minister Penny Wong attending. It was a pity that Pat Conroy as Minister for International Development and the Pacific did not attend; he had presumably overseen Australian support for the Samoa CHOGM. Not only did Australia provide significant support to Samoa in staging CHOGM, it also won support for a joint Australia-PIC bid to host COP in 2026. Australia is also building up political capital to give momentum for its bid to be on the UN Security Council in 2029-2030. Commonwealth countries make up more than one quarter of the United Nations.
While the issue of reparations for slavery might be seen as primarily a UK-Caribbean issue, the Caribbean countries (with twelve members) were in a strong position to further their argument at CHOGM. Other historical injustices that might be like slavery in some respects were included in the final communiqué: indigenous dispossession, indentureship blackbirding, and colonialism (a very broad category) (paras. 21-22). It remains to be seen how this issue will unfold, particularly with the next CHOGM being in the Caribbean. One might envisage a process of ‘truth telling’, already underway, and different ways of configuring ‘reparations’. This issue will not go away but nor is it likely to be resolved in the short term.
As with Australia, the UK had a successful CHOGM, with high level representation from Prime Minister Keir Starmer and Foreign Secretary David Lammy, as well as Lord Ray Collins as minister for Africa and the Commonwealth. The issue of slavery as highlighted in the British media has been dealt with for the time being but certainly not resolved. While ‘Global Britain’ might have been a slogan for the previous Conservative government, the new Labour government has shown that it too is globally minded but with different emphases, including through the Commonwealth.
While Justice Kirby made the case for a values-based Commonwealth, many members approach international politics from a realpolitik perspective. Among the major Commonwealth countries, this applies to India but also affects the way Australia and Britain relate to the world. Involvement in the Commonwealth might primarily be a manifestation of ‘good international citizenship’, but this can also have practical benefits, building support on issues that are important to those major Commonwealth powers. They are ‘major’ in the Commonwealth but not necessarily elsewhere.
Derek McDougall is Professorial Fellow, School of Social and Political Sciences, University of Melbourne.